Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2018-07
-
Phagocytosis was observed at min after mixing
2022-03-29
Phagocytosis was observed at 60 min after mixing macrophages with microbes (A). The phagocytosis ability (PA) and phagocytosis index (PI) values of the macrophages engulfing the bacteria measured in flow cytometer were shown in histograms (B). Statistical analyses revealed that both the PA and PI va
-
br Pharmacology br Background to GPR function br
2022-03-29
Pharmacology Background to GPR35 function The emerging function of GPR35 in the nervous system Conclusions The role of GPR35 in the modulation of synaptic transmission, neurogenic and inflammatory pain, and potential signalling pathways involved in these processes are beginning to emerge
-
Based on the results of compound appeared to have
2022-03-29
Based on the results of , Benidipine HCl appeared to have the best overall profile, so our efforts were then devoted to using 5-(-propyl)pyrimidine as the right-hand nitrogen attachment to optimize the R group of (). Analog was synthesized using the reaction conditions from , while analogs and were
-
In summary through medicinal chemistry design and computer a
2022-03-29
In summary, through medicinal chemistry design and computer-assisted conformational modeling, the initial lead was evolved into a series of dihydrobenzofuran derivatives, , as potent GPR119 agonists. Optimization of general structure at various regions of the molecule, including the substituent on d
-
SGCs tightly ensheath the soma of DRG neurons Costa and
2022-03-29
SGCs tightly ensheath the soma of DRG neurons (Costa and Moreira, 2015, Hanani, 2005, Takeda et al., 2009). Intimate associations between SGCs and neurons facilitate bidirectional regulation of SGC function and neuronal excitability. After nerve injury, neuronal hyperexcitability can result in SGC a
-
To investigate if such an effect is
2022-03-29
To investigate if such an effect is observed in native GlyT1, we introduced S605D and S605A mutations into GlyT1 and transfected these DNA constructs into N2a cells. For an internal control of calpain cleavage, we also introduced the first 100 amino-acids of the rat GlyT2N terminus upstream of the m
-
Always some extra effort may make great progress in sensing
2022-03-29
Always, some extra effort may make great progress in sensing platform, for example, Ma's group discovered luminescent iridium (Ⅲ) complexes which were highly selective for G-quadruplex DNA and Al3+, then they utilized these complexes to develop a series of G-quadruplex-based probes and chemosensor r
-
br Introduction Maintaining blood glucose within an appropri
2022-03-29
Introduction Maintaining blood glucose within an appropriate range is crucial for survival. In diabetes, those who suffer episodes of severe hypoglycemia have an increased risk of death [1], [2]. The retinoid x receptor is especially dependent on an adequate, continuous supply of circulating glu
-
Another key component of proper DA cell physiology is the
2022-03-29
Another key component of proper DA cell physiology is the basal firing activity of SN DA neurons, which maintains extracellular levels of dopamine in the dorsal striatum that are essential for voluntary movement [106]. Changes in SN DA neuron activity directly impacts the amount of dopamine released
-
bepridil br Ghrelin actions in the central nervous system br
2022-03-29
Ghrelin actions in the central nervous system Ghrelin induces thymopoeisis GHS-R1a is expressed in immune cells, including thymocytes and T-cells [13]. Infusion of ghrelin increases the number of thymocytes and thymus size in 14-, 20-, and 24-month-old mice, and with decreased thymic adiposity
-
The significance of A and tau as therapeutic targets is
2022-03-29
The significance of Aβ and tau as therapeutic targets is not only derived from pathological evidence of postmortem brain but also from biochemical analysis of cultured human neurons. This is largely based on the induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology that has been established to study Aβ, t
-
Studies have shown that coexpression of the HAC gene
2022-03-29
Studies have shown that coexpression of the HAC1 gene in P. pastoris improved the L-Glutathione Reduced level of foreign proteins [24,25]. By coexpression with PDI and Ero1, the expression level of the coexpressed strains was increased by 60% [26]. In our study, the α-galactosidase gene was coexpre
-
br Pathological consequences of disruption in the
2022-03-29
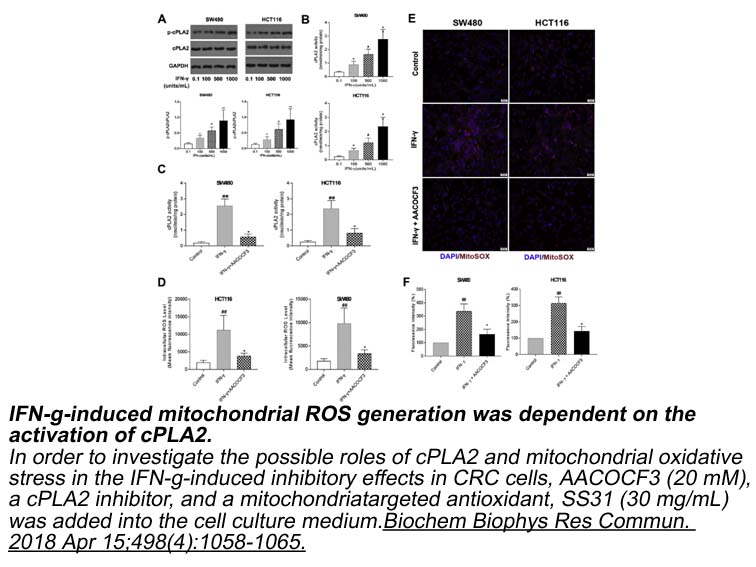
Pathological consequences of disruption in the GABA/T current equilibrium This issue has been particularly investigated in the context of absence seizures. These seizures are non-convulsive epileptic attacks present in many generalized genetic epilepsies that are characterized by a sudden and rel
-
For functional metagenomics based gene screening the DNA lib
2022-03-29
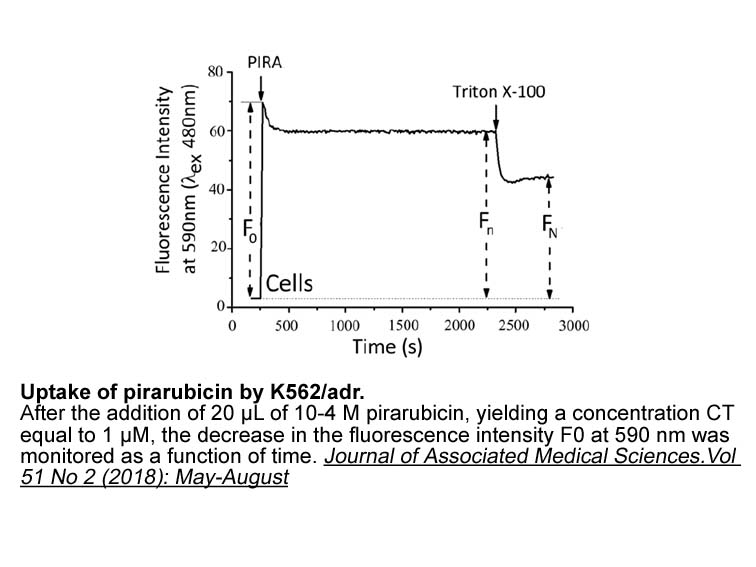
For functional metagenomics-based gene screening, the DNA library construction approach is widely used . Fosmid and cosmid libraries are usually used to explore novel genes. Lee et al. reported that a halotolerant and protease-resistant α-galactosidase was identified from the gut metagenome of , a p
-
Cytarabine Many neutral and acidophilic galactosidases have
2022-03-29
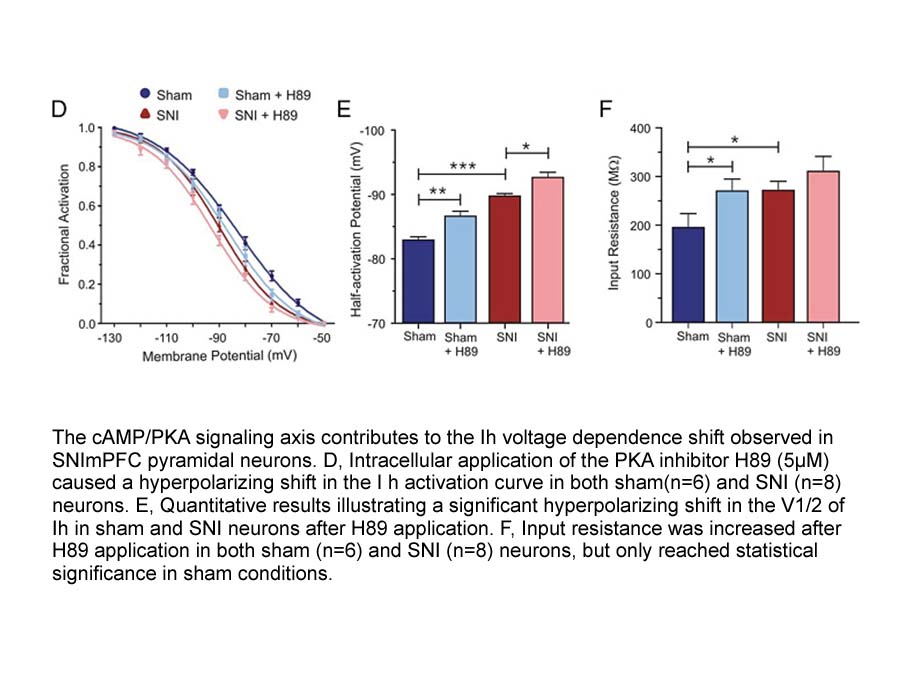
Many neutral and acidophilic β-galactosidases have been purified from microorganisms [14], while only a few alkalophilic β-galactosidases have been reported [19]. An alkalophilic β-galactosidase, BGal_375, was obtained and researched for the characterization of its hydrolytic activity. BGal_375 show
14684 records 472/979 page Previous Next First page 上5页 471472473474475 下5页 Last page